Biogas production is a sustainable way to generate renewable energy from organic waste. With the right tools and materials, you can set up a home biogas system that helps manage waste and produce fuel for cooking, heating, or electricity. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the essential tools and materials needed for making biogas at home.
1. Biogas Digester
The biogas digester is the core component of your system, where anaerobic digestion occurs. There are various types of digesters you can build or purchase:
- Plastic or Metal Drum: A simple and cost-effective option. The drum should be airtight to maintain anaerobic conditions.
- Fixed-Dome Digester: A more permanent structure, often made of concrete or brick, with a dome-shaped top.
- Plastic Bag Digester: Flexible and affordable, using heavy-duty plastic bags or liners.

2. Feedstock
- Kitchen Waste: Vegetable peels, fruit scraps, and leftover food.
- Manure: Cow, goat, or chicken manure, which is high in organic content.
- Garden Waste: Grass clippings, leaves, and plant trimmings.
- Animal Bedding: Straw or sawdust mixed with manure.
Ensure the feedstock is finely chopped or shredded to enhance the digestion process.
3. Inlet and Outlet Pipes
Proper piping is crucial for feeding materials into the digester and extracting biogas and digestate (the residual material):
- Inlet Pipe: For introducing feedstock into the digester. It should be sturdy and well-sealed.
- Outlet Pipe: For removing digested material from the system. It needs to be positioned to allow easy extraction of the digestate.
4. Gas Collection System
To capture and utilize the biogas, you’ll need:
- Gas Collection Bag or Tank: An airtight container or balloon to collect and store the biogas. It can be made of durable plastic or rubber.
- Gas Outlet Pipe: For directing the collected gas to where it will be used. Ensure it is well-sealed to prevent leaks.
5. Gas Regulator
A gas regulator helps control the flow and pressure of the biogas, making it safer and more manageable for use. It’s especially important if you plan to connect the biogas to appliances or a generator.
6. Mixing Tools
Mixing the feedstock ensures uniform digestion and efficient biogas production. Tools include:
- Shovel or Trowel: For mixing and transferring materials.
- Stirring Rod: To manually stir the contents of the digester, if necessary.
7. Monitoring Equipment
To ensure your biogas system is running smoothly, consider these monitoring tools:
- pH Meter: To check the acidity of the digester content. Ideal pH is around 6.8 to 7.5.
- Temperature Gauge: To monitor the temperature inside the digester, which should be between 35-40°C (95-104°F) for optimal digestion.
Gas monitoring: Biogas analyzers, such as the GASCHEK1000 portable biogas analyzer, use advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect and analyze methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases, and accurately report , while effectively checking the digestive process.
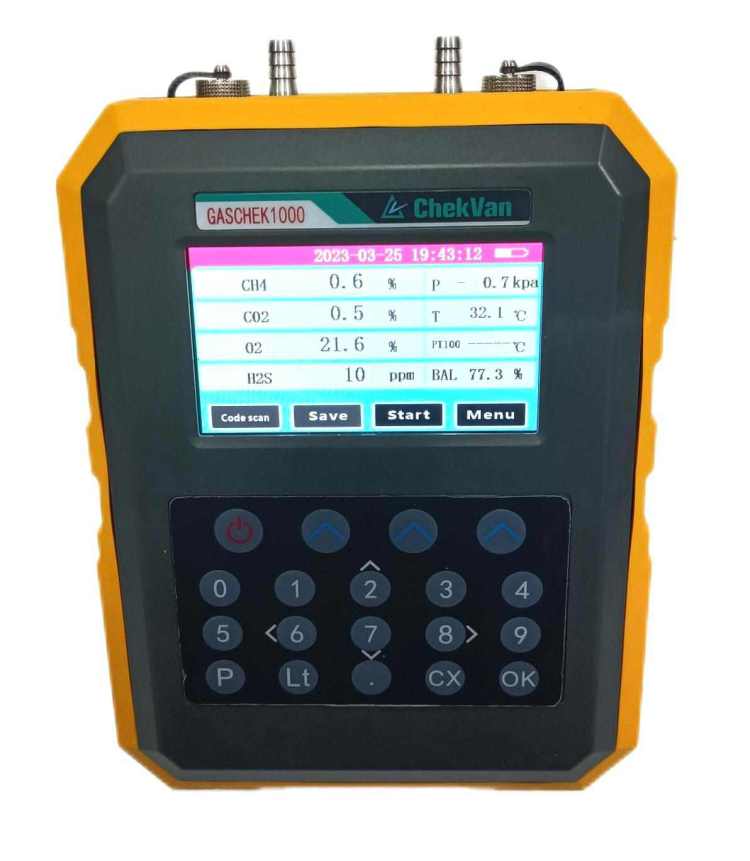
portable biogas analyzer Gaschek1000
8. Safety Equipment
Safety is paramount when working with biogas:
- Gloves and Protective Gear: To protect yourself from contact with waste and chemicals.
- Ventilation System: To ensure that any excess gas or fumes are safely dispersed.
9. Cleaning Supplies
Keeping your biogas system clean is important for maintaining efficiency:
- Cleaning Brushes: For scrubbing the interior of the digester and pipes.
- Disinfectants: To sanitize tools and surfaces.
10. Installation and Maintenance Tools
For setting up and maintaining your biogas system, you’ll need:
- Wrenches and Screwdrivers: For assembling and securing components.
- Sealants: To ensure all joints and connections are airtight.
Setting Up Your Biogas System
- 1. Choose a Suitable Location: Place the digester in a shaded, well-ventilated area to maintain optimal conditions.
- 2. Install the Digester: Assemble or place your digester according to the design you’ve chosen.
- 3. Connect Pipes and Collection System: Attach the inlet and outlet pipes, and set up the gas collection system.
- 4. Add Feedstock: Introduce your organic materials into the digester.
- 5. Monitor and Maintain: Regularly check the system for leaks, and ensure it remains clean and operational.
Conclusion
Creating a home biogas system involves a combination of essential tools and materials, each playing a crucial role in the successful production of biogas. By assembling the right components and maintaining your system, you can effectively manage organic waste and generate renewable energy, contributing to a more sustainable lifestyle.

