As the world continues to grapple with the impacts of climate change and the rising costs of fossil fuels, the quest for sustainable energy sources has never been more crucial. One promising solution lies in biogas—an often overlooked but powerful renewable energy resource. Biogas, produced from organic waste, can be converted into electricity, providing a clean, reliable, and efficient power source for homes and communities.
What is Biogas?
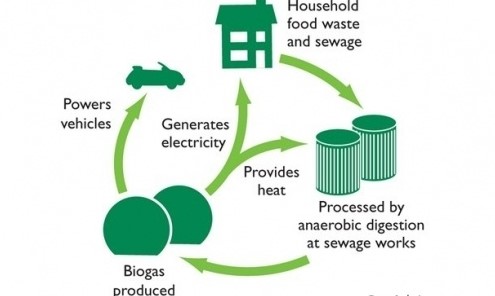
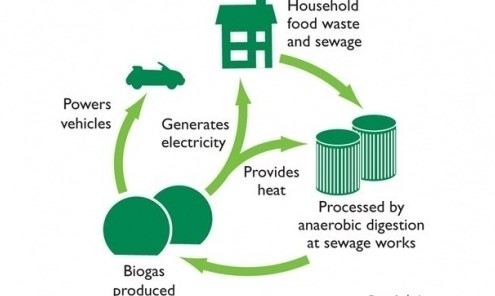
Biogas is a renewable energy source generated through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as food waste, animal manure, agricultural residues, and sewage sludge. This process takes place in an oxygen-free environment, where microorganisms break down the organic matter, releasing a mixture of gases—primarily methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). The high methane content in biogas makes it an excellent fuel for electricity generation.
The Biogas to Electricity Conversion Process
1. Biogas Collection and Storage:
Biogas is collected from anaerobic digesters, where organic waste undergoes breakdown by bacteria. Once produced, the biogas is stored in a gas holder or storage tank equipped with pressure regulation to maintain a consistent supply for electricity generation.
2. Biogas Purification:
Raw biogas contains impurities like hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), water vapor, and other trace gases that can corrode equipment and reduce efficiency. A biogas purification system removes these impurities, enhancing the quality of the biogas and ensuring it is suitable for use in electricity generation.
3. Biogas Engine or Generator:
Purified biogas is fed into a biogas engine or generator set designed specifically for biogas applications. These engines combust the methane in biogas, converting the chemical energy into mechanical energy, which then drives an alternator to produce electricity.
4. Electricity Generation and Distribution:
The electricity generated is either used on-site, stored in batteries, or fed into the electrical grid. This decentralized form of energy production can power homes, farms, and businesses, reducing reliance on traditional power plants.
5. Heat Recovery (Combined Heat and Power – CHP):
During the conversion process, a significant amount of heat is produced. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems capture this waste heat, which can be used for heating water, buildings, or greenhouses, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of the biogas plant.
Advantages of Biogas to Electricity Conversion
1. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Source:
Biogas is produced from organic waste, making it a renewable resource that helps close the loop in the waste-to-energy cycle. It provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional power generation.
2. Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
By capturing methane—a potent greenhouse gas—from organic waste, biogas production helps mitigate climate change. The use of biogas for electricity generation further reduces carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
3. Decentralized Energy Production:
Biogas plants can be set up near waste sources, allowing for local energy production. This decentralization reduces transmission losses, enhances energy security, and provides reliable power, especially in rural or off-grid areas.
4. Waste Management Solution:
Biogas production offers a sustainable way to manage organic waste, diverting it from landfills and reducing pollution. It transforms waste into a valuable resource, turning environmental liabilities into economic opportunities.
5. Economic Benefits:
Biogas-to-electricity systems can lower energy costs for households and businesses by providing a low-cost alternative to grid electricity. They also create jobs in biogas plant operation, maintenance, and construction, boosting local economies.
6. Scalability and Flexibility:
Biogas plants can range from small-scale systems suitable for individual households to large industrial plants powering entire communities. This scalability allows for flexibility in deployment, catering to different energy needs and waste availability.
The Path Forward: A Greener Future with Biogas
The biogas-to-electricity conversion process holds immense potential to revolutionize how we generate and consume energy. By turning waste into a valuable energy resource, biogas not only addresses waste management challenges but also contributes to the global push towards renewable energy. As technology advances and awareness grows, biogas is set to play a pivotal role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Governments, businesses, and communities must work together to overcome the barriers to biogas adoption, investing in research, infrastructure, and education. By embracing biogas, we can power our homes, reduce our environmental impact, and pave the way for a cleaner, greener world.
In conclusion, the biogas-to-electricity conversion process exemplifies the potential of circular economy principles in action. It’s time to unlock the power of biogas and harness this untapped resource to light up our homes and drive the future of sustainable energy.