As the global push for renewable energy continues to gain momentum, innovative technologies that turn waste into valuable resources have become increasingly important. One such technology is the anaerobic biogas digester, a system that not only provides a sustainable source of energy but also offers numerous environmental and economic benefits. By converting organic waste into biogas through anaerobic digestion, these digesters are helping communities and industries worldwide achieve cleaner energy production and more efficient waste management.
What is an Anaerobic Biogas Digester?
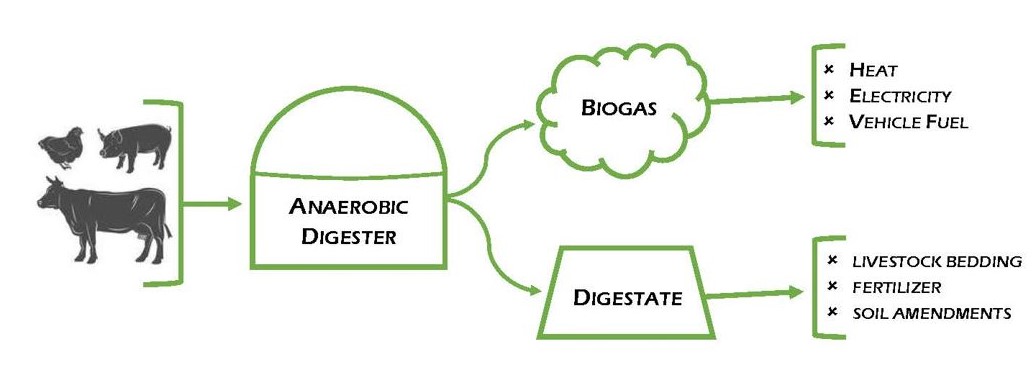
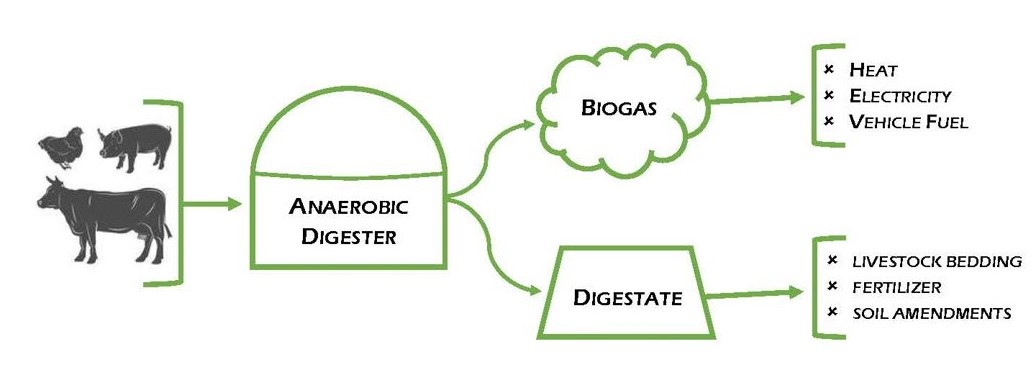
An anaerobic biogas digester is a closed system that breaks down organic matter—such as agricultural waste, animal manure, food waste, and sewage—without oxygen. This process is known as anaerobic digestion, and it results in the production of biogas, a mixture primarily composed of methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). The biogas produced can be used as a renewable energy source for cooking, heating, generating electricity, or even as a vehicle fuel when purified into biomethane.
In addition to biogas, anaerobic digesters also produce a by-product called digestate, a nutrient-rich material that can be used as a natural fertilizer, further contributing to sustainable agriculture.
How Anaerobic Biogas Digesters Work
- 1. Hydrolysis: Organic matter is broken down into smaller molecules like sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids.
- 2. Acidogenesis: The small molecules are further broken down by bacteria to produce volatile fatty acids, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and ammonia.
- 3. Acetogenesis: Acetogenic bacteria convert the acids into acetic acid, along with hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
- 4. Methanogenesis: Finally, methanogenic bacteria convert acetic acid, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide into methane gas and carbon dioxide, producing biogas.
The entire process occurs in an oxygen-free environment, making it efficient in decomposing organic waste while capturing methane for energy production.
It is necessary to monitor the composition of biogas. For example, the OLGA2000 biogas online monitoring system uses advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), etc. It can be widely used in gas monitoring in landfill biogas power plants, petrochemical industry, coal mines and other scenarios, and can realize remote data transmission.

Biogas online monitoring system OLGA2000
The Role of Anaerobic Biogas Digesters in Renewable Energy
1. Biogas as a Renewable Energy Source
– Biogas generated by anaerobic digesters is a renewable and sustainable form of energy that can replace fossil fuels in various applications. It is used for cooking, heating, powering electrical generators, and even fueling vehicles when purified to biomethane.
– Unlike intermittent energy sources like solar and wind, biogas production is continuous and can be relied upon for consistent energy output.
2. Waste Management
– Anaerobic biogas digesters serve a dual purpose by converting waste into energy, addressing the issue of organic waste disposal while simultaneously producing valuable resources.
– Digesters help manage agricultural and municipal waste efficiently, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and minimizing the environmental impacts of waste decomposition, such as methane emissions.
3. Carbon Emission Reduction
– By capturing methane that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere from decomposing waste, anaerobic digesters play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
– Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential many times higher than carbon dioxide. By using it as a fuel source instead of releasing it, anaerobic digesters help mitigate climate change.
Environmental Benefits of Anaerobic Biogas Digesters
- 1. Reduction of Landfill Waste: Organic waste that would otherwise end up in landfills can be processed in digesters, reducing the strain on waste disposal systems and lowering the risk of pollution from leachate and landfill gases.
- 2. Reduction of Air Pollution: Traditional waste disposal methods, such as open-air decomposition or burning, release harmful gases into the atmosphere. Anaerobic digestion captures these gases for energy production, reducing air pollution.
- 3. Water Protection: When organic waste is improperly managed, it can contaminate water sources through runoff. Anaerobic digestion contains and processes the waste, preventing pollutants from reaching groundwater and streams.
Challenges and the Future of Anaerobic Digesters
Despite their many advantages, anaerobic biogas digesters face challenges that need to be addressed to expand their use:
- 1. High Initial Costs: Building an anaerobic digestion facility requires significant upfront investment. However, as technology advances and biogas becomes more mainstream, costs are expected to decrease.
- 2. Efficiency Issues: Biogas production efficiency can vary depending on the type of feedstock and the technology used. Ongoing research and development aim to optimize the process and enhance the quality and quantity of biogas produced.
- 3. Public Awareness: Increasing public awareness about the benefits of anaerobic digestion and biogas is essential to driving widespread adoption.
Looking ahead, the future of anaerobic biogas digesters is bright, particularly as governments and industries continue to prioritize renewable energy and sustainability. With improvements in technology, decreasing costs, and growing recognition of the environmental and economic benefits, anaerobic digestion is set to play a crucial role in the global transition to cleaner energy systems.
Anaerobic biogas digesters offer a sustainable solution to many of the world’s most pressing environmental challenges, including waste management, energy production, and greenhouse gas emissions. By converting organic waste into biogas and nutrient-rich digestate, these systems embody the principles of the circular economy, turning waste into valuable resources. As the world seeks to transition to renewable energy sources, anaerobic biogas digesters will remain at the forefront of this movement, playing a key role in powering a sustainable future.