In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, renewable energy sources are becoming vital to meet growing energy demands while minimizing environmental impacts. Among these sources, biogas stands out as a versatile and eco-friendly alternative that can be converted into electricity to power homes and businesses. Biogas, produced from organic waste, represents a sustainable way to generate electricity, helping reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This article delves into the process of converting biogas into electricity and explores its significance in the context of modern energy solutions.
What is Biogas?
Biogas is a type of biofuel produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter by microorganisms. This process takes place in an oxygen-free environment and breaks down organic materials like agricultural residues, food waste, manure, and sewage sludge, producing a gas mixture primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), along with trace amounts of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S).
The high methane content in biogas makes it an excellent candidate for energy production, as methane is a potent energy carrier that can be burned to generate heat and electricity.
The Biogas to Electricity Conversion Process
1. Biogas Production:
The journey begins with the production of biogas in an anaerobic digester. Organic waste materials are collected and fed into the digester, where they undergo microbial decomposition in an oxygen-free environment. The digester is a sealed, insulated tank designed to maintain optimal temperatures and conditions for the microbes to thrive and produce biogas efficiently. Depending on the type of waste and the digester’s design, the biogas production process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks.
During the biogas production process, a biogas analyzer is needed to monitor the composition of the biogas. For example, the OLGA2000 biogas online monitoring system uses advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect and analyze methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases.
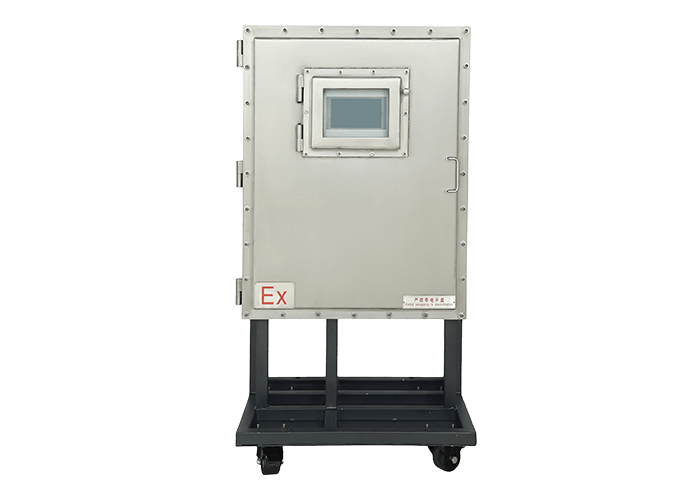

2. Biogas Cleaning and Conditioning:
Raw biogas typically contains impurities such as water vapor, hydrogen sulfide, and siloxanes that can be corrosive or harmful to engines and generators. Therefore, before the biogas can be used for electricity generation, it must be cleaned and conditioned. This process involves several steps:
Water Removal: Moisture in the biogas is removed using cooling systems or moisture traps.
H2S Removal: Hydrogen sulfide, which is toxic and corrosive, is often removed using chemical scrubbers or biological filters.
Siloxane Removal: Siloxanes, commonly found in biogas derived from sewage or landfills, can form abrasive deposits in engines. Activated carbon filters or adsorption techniques are used to remove them.
3. Biogas Utilization in Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems:
Once cleaned, the biogas is ready to be converted into electricity. This is typically done using Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems, also known as cogeneration systems, which simultaneously generate electricity and useful heat from the same energy source. The process works as follows:
Internal Combustion Engine or Gas Turbine: The cleaned biogas is fed into an internal combustion engine or a gas turbine, where it is combusted to produce mechanical energy.
Electric Generator: The mechanical energy from the engine or turbine drives an electric generator, converting the energy into electricity.
Heat Recovery: In addition to electricity, CHP systems capture the waste heat generated during combustion, which can be used for heating water, space heating, or other industrial processes, thereby increasing the system’s overall efficiency.
4. Electricity Distribution:
The electricity generated from biogas can be used on-site to power homes, farms, or industrial facilities. Alternatively, it can be fed into the local electrical grid, providing renewable energy to the surrounding community. In some cases, surplus electricity can also be sold back to the grid, creating an additional revenue stream for biogas plant operators.
5. Digestate Management:
The byproduct of anaerobic digestion is digestate, a nutrient-rich slurry that can be used as a high-quality organic fertilizer in agriculture. The use of digestate not only closes the nutrient loop but also reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, further enhancing the sustainability of the biogas production process.
Advantages of Biogas to Electricity Conversion
Converting biogas to electricity offers numerous environmental, economic, and social benefits:
1. Renewable Energy Source:
Biogas is a renewable energy source, derived from organic waste that is continuously generated by agricultural activities, food production, and wastewater treatment. This makes it a sustainable and reliable energy solution.
- Greenhouse Gas Mitigation:
By capturing and utilizing methane from organic waste, biogas production significantly reduces methane emissions—a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential many times greater than CO2. Additionally, biogas combustion for electricity generation results in lower CO2 emissions compared to fossil fuels.
3. Energy Independence and Security:
Biogas plants can provide localized energy solutions, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhancing energy security for communities and industries.
4. Waste Management and Resource Efficiency:
Biogas production helps manage organic waste effectively, diverting it from landfills and reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal. The process also recycles nutrients, contributing to soil health and agricultural productivity.
5. Economic Benefits:
Biogas plants create jobs in construction, operation, and maintenance, and can provide additional income for farmers and waste management facilities through the sale of electricity and organic fertilizers.
Despite these challenges, the future of biogas to electricity conversion is bright. Continued technological advancements, coupled with increasing awareness of the need for sustainable energy solutions, are likely to drive the growth of biogas projects worldwide. As more communities and industries embrace this technology, biogas has the potential to play a significant role in powering a greener, more sustainable future.
