In the global pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, bio natural gas emerges as a promising contender, offering a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Derived from organic materials such as agricultural waste, food scraps, and wastewater, bio natural gas harnesses the power of nature to generate clean energy. In this article, we delve into the potential of bio natural gas, its production process, applications, and its role in shaping a greener future.
The Essence of Bio Natural Gas:
Bio natural gas, also known as renewable natural gas (RNG) or biomethane, is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials. During this process, microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the release of methane-rich gas. The captured methane can then be purified to meet natural gas quality standards, making it suitable for injection into natural gas pipelines, use as a transportation fuel, or direct combustion for heating and electricity generation.

Advantages of Bio Natural Gas:
1. Renewable and Sustainable:
– Unlike finite fossil fuels, bio natural gas is derived from renewable organic sources, making it a sustainable energy option. Its production relies on readily available feedstock, such as agricultural residues and organic waste, which can be continuously replenished.
2. Greenhouse Gas Reduction:
– Bio natural gas production offers significant environmental benefits by mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. By capturing methane from organic waste, bio natural gas projects prevent the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. This process effectively reduces the carbon footprint and helps combat climate change.
3. Energy Independence:
– The utilization of bio natural gas promotes energy independence and resilience by diversifying energy sources. Communities and industries can produce their own renewable natural gas locally, reducing dependency on imported fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
4. Waste Management Solution:
– Bio natural gas production provides a sustainable solution for organic waste management. By diverting organic materials from landfills and anaerobic digestion, bio natural gas projects contribute to waste reduction, odor control, and environmental protection.
Production Process of Bio Natural Gas:
- 1. Feedstock Collection:
– Organic feedstock, including agricultural residues, food waste, and wastewater, is collected and transported to biogas facilities for processing.
- 2. Anaerobic Digestion:
– In anaerobic digesters, microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas as a byproduct. The biogas primarily consists of methane and carbon dioxide, along with trace gases.
- 3. Gas Purification:
– Biogas undergoes purification processes to remove impurities such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and moisture. The purified methane-rich gas, known as biomethane, meets natural gas quality standards.
- 4. Gas monitoring
Biogas analyzers, such as the GASCHEK1000 portable biogas analyzer, use advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect and analyze methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases, and accurately report , while effectively checking the digestive process.
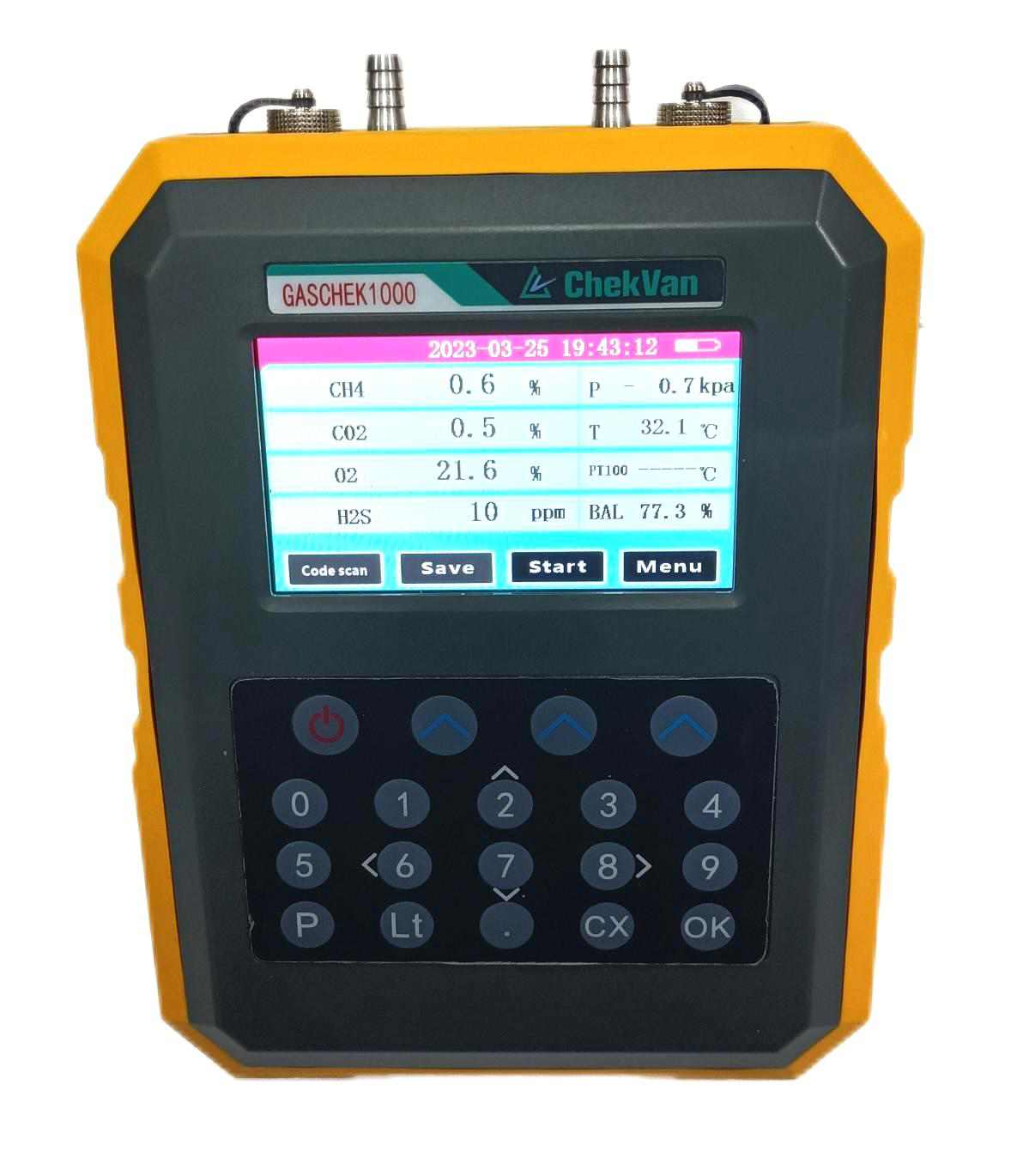
- 5. Gas Utilization:
– Biomethane can be utilized for a variety of applications, including heating, electricity generation, and transportation. It can be injected into natural gas pipelines, used as a vehicle fuel (compressed natural gas or liquefied natural gas), or combusted in combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the transition to a sustainable energy future, bio natural gas emerges as a valuable resource with immense potential. By harnessing the power of organic waste, bio natural gas projects offer a triple bottom line of environmental, social, and economic benefits. By unlocking nature’s energy through bio natural gas, we pave the way for a cleaner, greener, and more resilient energy landscape.

