In the pursuit of sustainable living and energy independence, more individuals are exploring alternative energy sources. One such avenue gaining popularity is the creation of homemade biogas digesters. These DIY systems harness the power of anaerobic digestion to convert organic waste into biogas, a renewable energy source. In this article, we’ll embark on a journey into the world of building your own homemade biogas digester, exploring the steps, benefits, and considerations for a successful home biogas project.
1. Understanding the Basics:
– Before diving into the construction process, it’s crucial to understand the basic principles of anaerobic digestion. Biogas is produced when organic materials, in the absence of oxygen, decompose through the activity of microorganisms. Common feedstocks for homemade digesters include kitchen waste, agricultural residues, and animal manure.
2. Choosing the Right Design:
- – Homemade biogas digesters come in various designs, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Common designs for small-scale applications include:
- – Floating Drum Digester: Utilizes a floating drum to collect and store biogas.
- – Batch Digester: Processes organic waste in batches, suitable for intermittent use.
- – Continuous Flow Digester: Allows for a continuous feeding of organic material, suitable for a steady supply of biogas.

3. Gathering Materials:
- – The materials needed for a homemade biogas digester are often readily available and cost-effective. Key components include:
- – Digester Tank: Usually made of plastic, metal, or concrete, serving as the vessel for anaerobic digestion.
- – Gas Collection System: A container or drum that captures and stores the produced biogas.
- – Inlet and Outlet Pipes: Facilitate the feeding of organic waste into the digester and the removal of digested material (slurry).
4. Constructing the Digester:
– The construction process involves assembling the digester components based on the chosen design. This may include connecting pipes, ensuring airtight seals, and incorporating safety features. Step-by-step guides and plans are available online and in renewable energy resources to assist in the construction.
5. Feeding the Digester:
– Once the digester is set up, it’s time to start feeding it with organic waste. Kitchen scraps, food leftovers, and manure are excellent sources of feedstock. It’s essential to maintain a balance between carbon-rich (brown) and nitrogen-rich (green) materials for optimal digestion.
6. Collecting and Utilizing Biogas:
- – As the anaerobic digestion process takes place, biogas will be produced and collected in the gas storage system. The collected biogas can be used for various purposes, including:
- – Cooking: Connect the biogas to a gas stove for cooking.
- – Heating: Use biogas for heating applications, such as space heaters.
- – Lighting: Utilize biogas for gas lamps or lanterns.
7. Maintaining the Digester:
- – Regular maintenance is crucial for the efficient operation of a homemade biogas digester. This includes:
- – Stirring: Periodically stir the contents of the digester to promote even digestion.
- – Temperature Monitoring: Ensure that the digester is kept within the optimal temperature range for microbial activity.
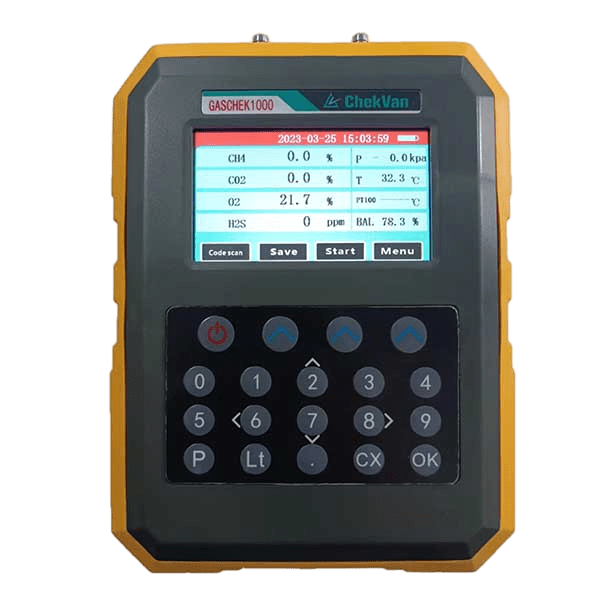
- – Gas Quality Monitoring: Check the quality of biogas regularly, and address any issues promptly. Such as the GASCHEK1000 portable biogas analyzer, use advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect and analyze methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases, and accurately report , while effectively checking the digestive process.
8. Scaling Up or Adapting:
– Depending on the success and requirements, individuals may choose to scale up their homemade biogas systems or adapt the design to better suit their needs. This could involve connecting multiple digesters or integrating additional features for improved performance.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals in the Energy Revolution
Building a homemade biogas digester is more than a DIY project; it’s a step towards personal sustainability and active participation in the renewable energy revolution. While these systems may not replace large-scale biogas plants, they empower individuals and communities to contribute to a greener future. By turning organic waste into a valuable energy resource, homemade biogas digesters exemplify the transformative potential of sustainable living.

