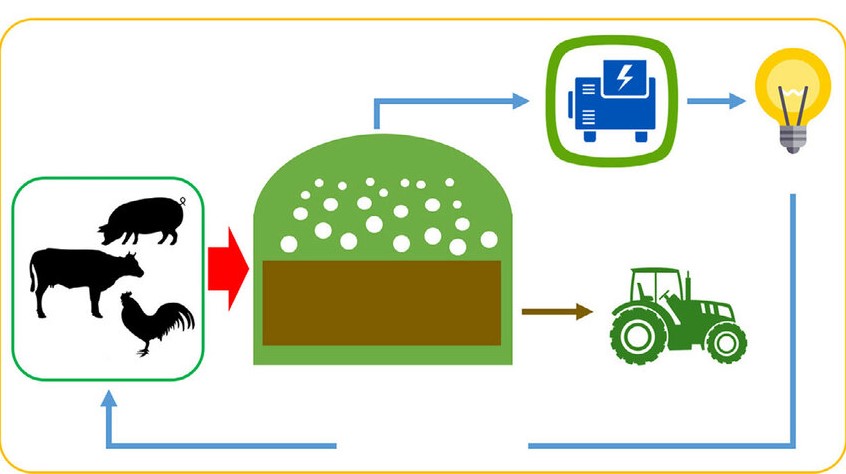
In the pursuit of sustainable and renewable energy sources, biogas production from manure emerges as a transformative solution that not only addresses waste management challenges but also provides a clean and renewable energy resource. Manure, often considered an agricultural byproduct, can be harnessed to produce biogas through anaerobic digestion. In this article, we explore the process of harnessing biogas from manure, its environmental benefits, and its potential to revolutionize the way we view and utilize waste.
1. Anaerobic Digestion of Manure:
The process begins with anaerobic digestion, a natural biological process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. Manure, rich in organic matter, serves as the feedstock for this process. In a controlled environment such as a biogas digester, microorganisms break down the organic components of manure, producing biogas as a byproduct. This biogas primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
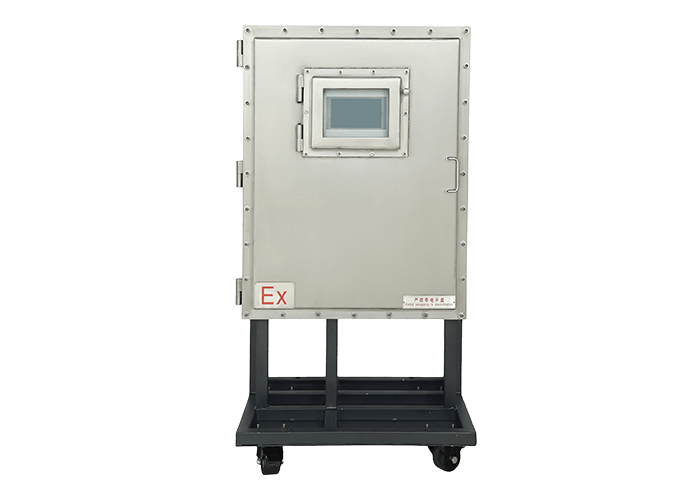
During the biogas production process, the required equipment is a biogas analyzer, which uses advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect and analyze methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases. For example OLGA2000 Online Biogas Monitoring System can be widely used in gas monitoring in landfill gas power plants, petrochemicals, coal mines and other scenarios, and can realize remote data transmission.

2. Environmental Benefits:
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
– Manure management is a significant source of methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. By harnessing biogas from manure through anaerobic digestion, these emissions are mitigated, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Nutrient-Rich Byproduct:
– The residue from anaerobic digestion, known as digestate, is a nutrient-rich byproduct that can be used as an organic fertilizer. This closes the nutrient loop, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Improved Air and Water Quality:
– Anaerobic digestion reduces the odors associated with untreated manure, contributing to improved air quality in the surrounding areas. Additionally, the process helps in reducing nutrient runoff, enhancing water quality.
3. Biogas Utilization:
Electricity Generation:
– The captured biogas can be utilized to generate electricity. This is commonly achieved by using the biogas to fuel engines or turbines that produce electrical power. On-farm electricity generation can contribute to energy independence.
Heat Production:
– Biogas can be used for heating purposes, providing a sustainable energy source for space heating in buildings or for various industrial processes.
Cooking and Lighting:
– In rural areas, where access to conventional energy sources may be limited, biogas can be used for cooking and lighting, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative.
4. Small-Scale and On-Farm Biogas Systems:
Decentralized Energy Production:
– Small-scale biogas systems, especially on farms, offer a decentralized approach to energy production. This not only reduces transmission losses but also provides a reliable and locally sourced energy supply.
Waste Management for Farms:
– On-farm biogas systems provide a solution for managing animal waste. By converting manure into biogas, farmers can address waste disposal challenges while harnessing a valuable energy resource.
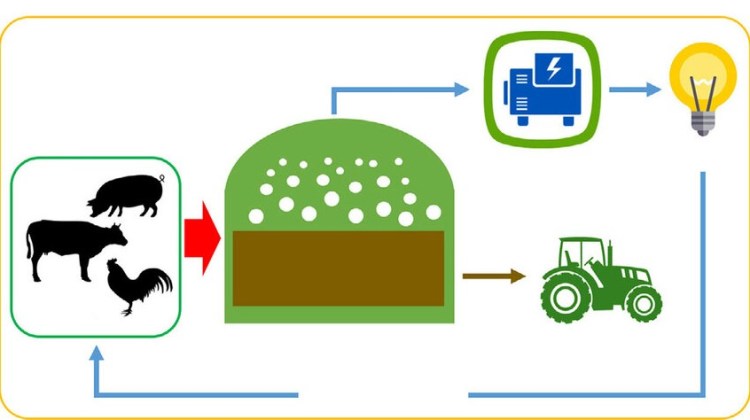
5. Future Prospects:
As technology continues to advance and the benefits of biogas from manure become more apparent, there is growing interest in expanding the use of on-farm biogas systems. Innovations in digester design, gas utilization, and integration with other renewable energy sources are likely to enhance the efficiency and viability of these systems.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Path Forward:
Harnessing biogas from manure represents a sustainable path forward, where waste is transformed into a valuable resource for energy production. Beyond the environmental benefits, on-farm biogas systems contribute to resilient and decentralized energy infrastructures, offering farmers a solution for waste management while reducing their carbon footprint. As we continue to explore and adopt cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions, the utilization of biogas from manure emerges as a practical and environmentally conscious choice, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.