Coral reefs, often hailed as the rainforests of the sea, harbor an intricate ecosystem of marine life. However, beyond their role in biodiversity, corals can play an unexpected part in sustainable energy solutions. This article delves into the innovative concept of extracting biogas from coral organic waste, showcasing the potential for environmental conservation and renewable energy generation.
Understanding Coral Organic Waste:
Coral organic waste comprises organic matter generated by coral reefs, including discarded or decaying coral fragments, algae, and other biological materials. Traditionally considered a natural part of reef ecosystems, this organic waste can now be viewed through a new lens—as a resource for clean energy production.
The Biogas Production Process:
1. Waste Collection:
Gather coral organic waste, which may include broken coral pieces, algae, and other marine debris.
2. Anaerobic Digestion:
Introduce the collected waste into an anaerobic digester. This closed system facilitates the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen.
3. Biogas Formation:
As the organic waste undergoes anaerobic digestion, it produces biogas, primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
4. Gas monitoring:
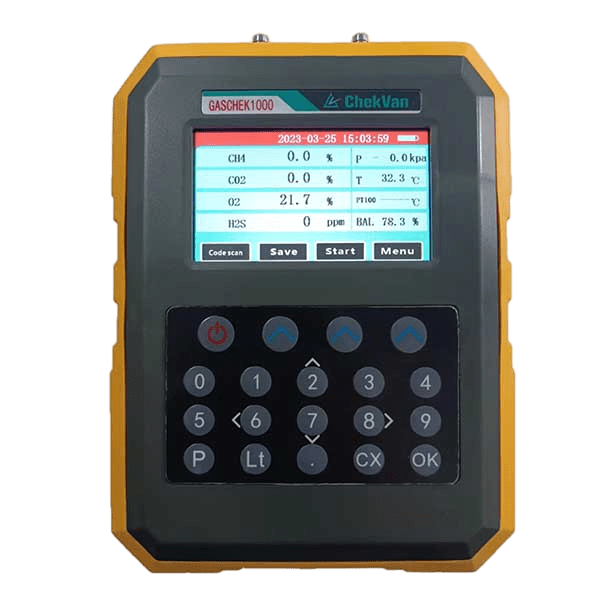
Biogas analyzers, such as the GASCHEK1000 portable biogas analyzer, use advanced photoelectric sensing principles to detect and analyze methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases, and accurately report , while effectively checking the digestive process.
5. Gas Capture:
Capture and store the generated biogas for various applications.
6. Utilization:
Biogas can be utilized for cooking, heating, electricity generation, or even as a fuel for marine vessels.
Benefits of Biogas from Coral Organic Waste:
1. Waste Management:
– Converting coral organic waste into biogas offers an effective solution for managing marine debris and decaying coral fragments.
2. Renewable Energy Source:
– Biogas is a clean and renewable energy source, contributing to the diversification of the energy mix.
3. Environmental Conservation:
– By repurposing coral organic waste, this approach aligns with conservation efforts, minimizing the ecological impact of marine debris.

4. Localized Energy Production:
– Biogas generation from coral waste can be harnessed locally, contributing to energy independence in coastal communities.
5. Climate Change Mitigation:
– The reduction of methane emissions from decaying organic matter in coral reefs contributes to climate change mitigation efforts.
Unlocking coral’s potential for biogas production represents a unique intersection of environmental conservation and sustainable energy solutions. By reimagining coral organic waste as a valuable resource, this innovative approach contributes to both the preservation of marine ecosystems and the transition toward cleaner, renewable energy.
