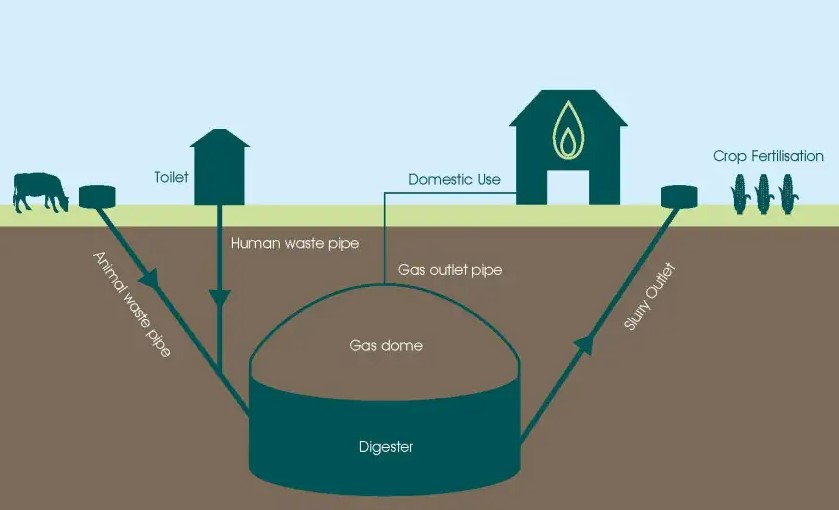
In the pursuit of sustainable living, individuals and communities are exploring innovative ways to reduce their environmental impact while embracing eco-friendly practices. One such solution that has gained momentum is the adoption of portable biogas plants. These compact, efficient systems allow households to convert organic waste into clean energy while actively participating in responsible waste management.
Portable biogas plants, also known as domestic biogas digesters, are scaled-down versions of larger industrial biogas facilities. They utilize the same biological process of anaerobic digestion to convert organic waste into biogas, primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The key components of a portable biogas plant typically include:
- 1. Digester: This is the core of the system, where organic waste is processed and biogas is produced. Portable digesters come in various sizes to suit different household needs.
- 2. Gas Storage: Biogas generated in the digester is stored in a gas holder, which can be a floating drum or a fixed-dome design.
- 3. Inlet and Outlet: These are used for feeding organic waste into the digester and collecting the nutrient-rich slurry (digestate) produced after digestion.
- 4. Gas Delivery System: This system allows homeowners to channel the biogas for cooking, heating, or other applications.
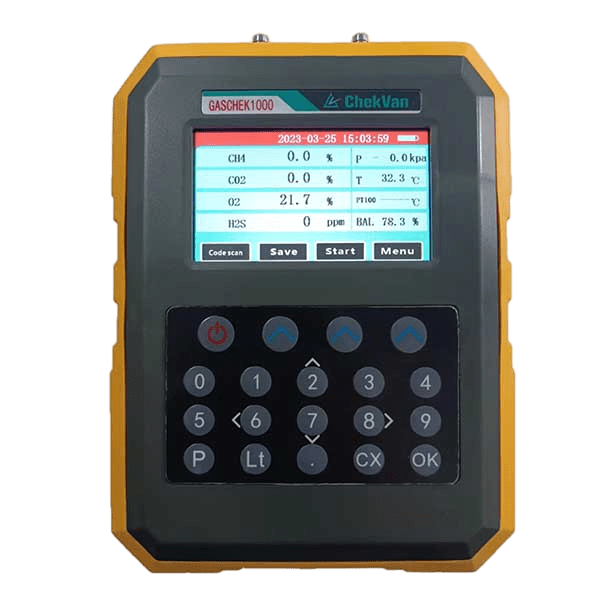
- 5. Monitoring equipment: During the biogas production process, the required equipment is a biogas analyzer.GASCHEK1000 portable biogas analyzer adopts advanced photoelectric sensing principle to realize the detection and analysis of methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and other gases for accurate reporting while checking the digestion process efficiently.
Benefits of Portable Biogas Plants
- 1. Clean Energy: Portable biogas plants provide a renewable and clean energy source, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
- 2. Waste Reduction: These systems efficiently manage organic waste, diverting it from landfills where it would otherwise decompose anaerobically, releasing methane into the atmosphere.
- 3. Cost Savings: By producing their energy for cooking or heating, households can reduce their utility bills over time, resulting in cost savings.
- 4. Reduced Carbon Footprint: The use of biogas significantly reduces the carbon footprint of a household, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
- 5. Nutrient Recycling: The nutrient-rich digestate produced as a byproduct of the digestion process can be used as an organic fertilizer, closing the loop in nutrient recycling.

Building a Portable Biogas Plant: The Basics
1. Selecting a Location
2. Digester Design
3. Gathering Feedstock
4. Digestion Process
5. Biogas Collection
6. Gas Utilization
7. Maintenance
Portable biogas plants are a commendable step toward sustainable living. They not only provide renewable energy but also address waste management issues and reduce the carbon footprint of households. By embracing this eco-friendly technology, individuals and communities can contribute to a more sustainable future while enjoying the benefits of clean energy and responsible waste management. Portable biogas plants exemplify the principles of sustainable living, demonstrating that even small-scale actions can have a big impact on reducing environmental harm.