In a world increasingly concerned with sustainable living and environmental conservation,individuals and communities are exploring innovative ways to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt eco-friendly practices.One such sustainable solution gaining popularity is the construction of biogas plants at home.These small-scale digesters offer an opportunity for households to convert organic waste into clean energy while simultaneously addressing waste management issues.
The Essence of a Home Biogas Plant
A home biogas plant,often referred to as a domestic biogas digester or biodigester,is a scaled-down version of commercial biogas facilities.It utilizes the same fundamental principle of anaerobic digestion to convert organic materials into biogas.This biogas,primarily composed of methane(CH4)and carbon dioxide(CO2),can be used for various purposes,such as cooking,heating,or even generating electricity.
Benefits of a Home Biogas Plant
- 1.Clean and Renewable Energy:Home biogas plants provide a source of clean and renewable energy,reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- 2.Waste Management:These plants efficiently manage organic waste,diverting it from landfills or open dumping,which can contribute to environmental pollution.
- 3.Cost Savings:By producing your energy for cooking or heating,you can reduce your utility bills,ultimately saving money in the long run.
- 4.Reduced Carbon Footprint:The use of biogas significantly reduces the carbon footprint of your household,contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
- 5.Nutrient-Rich Fertilizer:The nutrient-rich slurry or digestate produced as a byproduct of the digestion process can be used as an organic fertilizer to enhance plant growth in your garden.
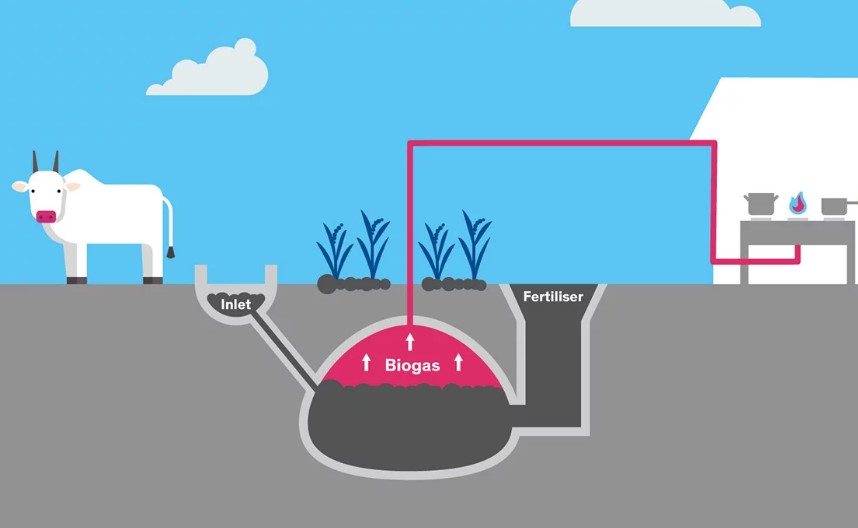
Building a Home Biogas Plant:The Basics
- 1.Selecting a Location:Choose a suitable location for your biogas digester,considering factors like sunlight exposure,proximity to the kitchen,and ease of waste collection.
- 2.Digester Design:Select an appropriate digester design based on your space,budget,and requirements.Popular designs include fixed-dome digesters,floating-drum digesters,and plug-flow digesters.
- 3.Gathering Feedstock:Collect organic waste materials such as kitchen scraps,food waste,vegetable peels,and animal manure to serve as feedstock.
- 4.Digestion Process:Load the organic waste into the digester and provide the necessary conditions for anaerobic digestion to occur.This typically involves maintaining a consistent temperature and mixing the feedstock.
- 5.Biogas Collection:Capture the biogas produced by the digester using a gas holder,which can be a floating drum or a fixed-dome structure.
- 6.Gas Utilization:Connect the biogas to your cooking stove,heating system,or other appliances that can run on gas.
- 7.Maintenance:Regularly maintain the digester by removing digested material,replenishing feedstock,and ensuring gas lines are free from blockages.
Challenges and Considerations
- -Initial Investment:There is a cost associated with constructing the digester and setting up the biogas system.
- -Feedstock Availability:The consistent availability of organic waste can be a challenge,particularly in urban areas.
- -Maintenance:Biogas plants require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
By embracing this eco-friendly technology,individuals and communities can contribute to a more sustainable future while enjoying the benefits of clean energy and responsible waste management.A home biogas plant is a practical embodiment of the principles of sustainable living,demonstrating that every action counts in the journey towards a greener planet.
