With increasing global focus on sustainable development, biogas digesters have become key in the fields of sustainable agriculture and waste management, providing a versatile and efficient way to harness renewable energy.
Digesters are anaerobic digestion systems that convert organic waste such as animal manure, crop residues, food waste and wastewater into biogas through a natural decomposition process. These digesters create an oxygen-free environment in which bacteria break down organic matter, releasing biogas—mainly a mixture of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
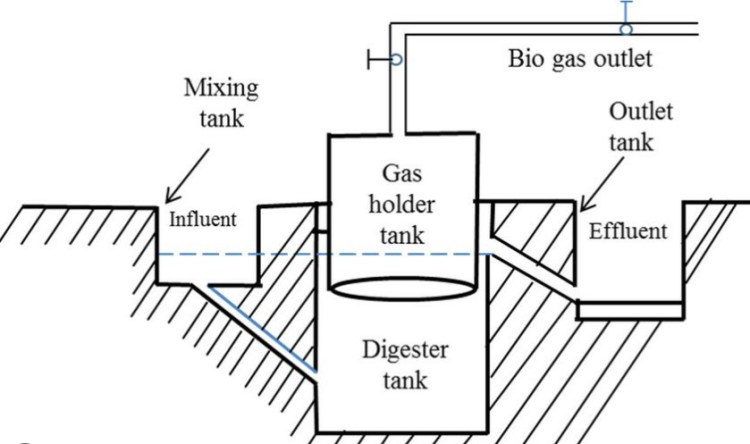
Benefits of Digesters
1. Renewable energy generation: Biogas digesters provide sustainable and renewable energy. The biogas produced can be captured, purified and used as fuel for electricity or heat production. This renewable energy can power farms, rural communities and even be injected into the natural gas grid, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and helping the transition to a low-carbon energy system.
2. Climate Change Mitigation: Digesters play an important role in climate change mitigation. The anaerobic digestion process captures methane, a potent greenhouse gas with significantly higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. Digesters prevent methane emissions from entering the atmosphere by converting organic waste into biogas. This helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming.
3. Waste management and nutrient recovery: Digesters provide effective waste management solutions, especially for agricultural operations. By converting organic waste into biogas, digesters reduce the volume of waste that might otherwise end up in landfill or emit greenhouse gases during natural decomposition. Biogas residue is the nutrient-rich residue left after biogas production, which can be used as organic fertilizer. Applying biogas residues to fields helps close nutrient cycles, promotes soil health, reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, and promotes sustainable agriculture.
4. Odor reduction and pathogen control: Digesters can significantly reduce odors associated with organic waste, especially livestock manure. The anaerobic digestion process reduces the production of malodorous gases, making it an advantageous option for managing agricultural waste close to residential areas. Additionally, the high temperature and microbial activity during digestion destroys harmful pathogens, thereby minimizing the risk of water and soil contamination.

5. Economic benefits and rural development: biogas digesters provide economic benefits and promote rural development. By generating renewable energy, digesters can offset a farm or community’s energy costs, creating a potential source of income. Digesters can also diversify their income streams by selling excess electricity or heat. Additionally, the implementation of biogas digesters can stimulate job creation, foster local entrepreneurship, support sustainable agricultural practices, and drive economic growth in rural areas.
6. Improved water management: Digesters can help improve water management in agriculture. By diverting organic waste to digesters, the nutrient load in wastewater can be reduced and nutrient runoff into water bodies prevented. This reduces the risk of water pollution, eutrophication and related environmental problems. In addition, biogas residue from biogas production can be applied to farmland to enhance soil water retention and reduce irrigation needs.
The ability of digesters to convert organic waste into valuable resources while reducing greenhouse gas emissions makes them a key tool for achieving environmental sustainability and resource efficiency. As the world faces the challenge of climate change and seeks to create resilient and sustainable agricultural systems, biogas digesters are emerging as a transformative technology.
