As the world looks for alternatives to fossil fuels, the need for sustainable and renewable energy has never been more urgent. Biogas has emerged as a promising solution in recent years, revolutionizing energy production and waste management. Biogas, which generates clean energy from organic waste, is gaining momentum and is reshaping the way we think about sustainable energy. We’ll explore the rise of biogas and its transformative impact on energy production and waste management.

Biogas is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion, where organic waste such as agricultural residues, food waste and wastewater is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. This natural process releases a mixture of gases, primarily methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), which can be captured and used as a renewable energy source.
Renewable energy generation: One of the most notable advantages of biogas is its potential to generate renewable energy. Biogas can be used to generate electricity, heat or as fuel for vehicles. By utilizing biogas, we can reduce our dependence on non-renewable fossil fuels, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable energy mix.
Waste management and environmental sustainability: Biogas production plays a vital role in waste management. Biogas plants reduce greenhouse gas emissions by diverting organic waste from landfills as organic waste decomposes and releases methane into the atmosphere. Additionally, the anaerobic digestion process reduces the amount of waste and eliminates harmful pathogens, producing a valuable by-product, Biogas residue.
Biogas residue can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer, forming a closed loop in a sustainable waste management system.
Agricultural benefits: Biogas production brings huge benefits to the agricultural sector. Farmers can utilize the biogas residue produced during anaerobic digestion as a natural and nutrient-rich fertilizer for crops. This helps improve soil quality, increase yields and reduce reliance on chemical fertilizers. In addition, biogas plants can use agricultural residues such as crop residues or manure as feedstock for biogas production, providing farmers with an additional source of income and helping them manage organic waste efficiently.
Circular economy and resource efficiency: Biogas production embodies the principles of a circular economy, converting waste into valuable resources. By converting organic waste into energy, biogas plants help increase resource efficiency and reduce the need for virgin materials. In addition, the heat generated during biogas production can be used for a variety of purposes, such as heating greenhouses or nearby buildings, maximizing energy efficiency and reducing overall energy demand.
Climate Change Mitigation: Biogas production plays a vital role in mitigating climate change. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, and its capture and use can significantly reduce its emissions to the atmosphere. Methane has a higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide, so its effective management through biogas production can help minimize its impacts to combat climate change.
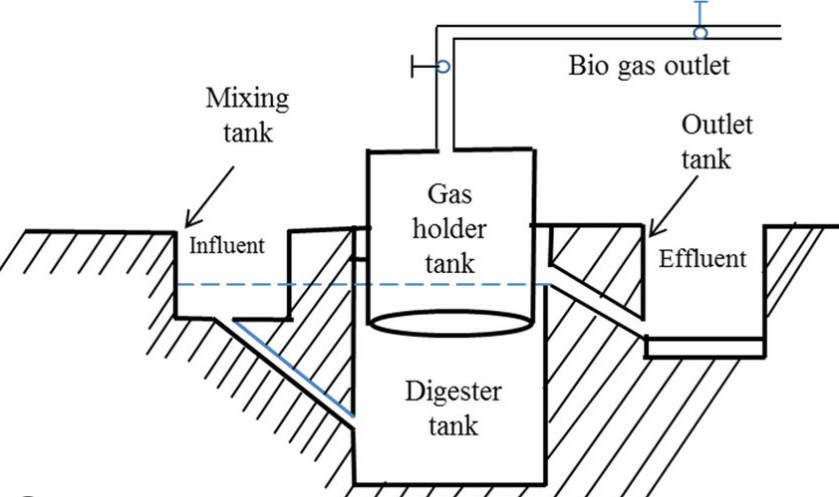
The rise of biogas is revolutionizing energy production and waste management. This versatile energy source offers many benefits, including renewable energy generation, sustainable waste management, agricultural advantages, resource efficiency and climate change mitigation. By adopting biogas, we can unlock a cleaner, more efficient future and pave the way for a circular economy that maximizes resource use and minimizes environmental impact.
